Table of Contents
ToggleWhy You Should Switch to 3D Printed Architecture Model?
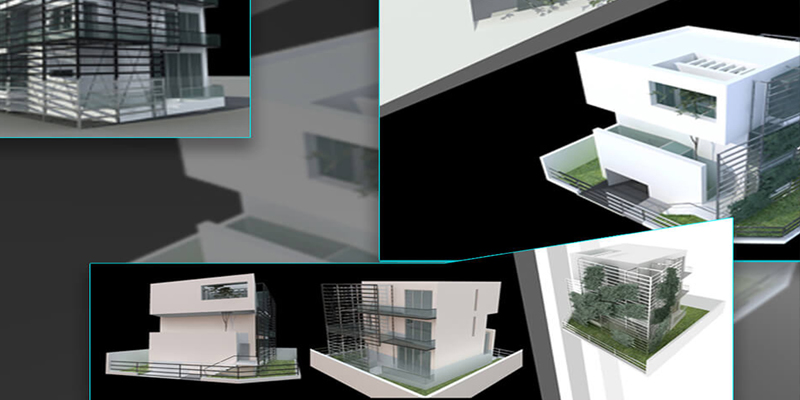
Architectural modeling is the creation of scaled representations of building designs, used to study aspects of architectural design and communicate design ideas. Historically, these models were meticulously handcrafted from materials like wood, paper, and foam. Over time, as building designs increased in complexity, these manual techniques began to fall short.
The advent of computer-aided design (CAD) software in the late 20th century marked a pivotal shift. This transitioned architectural modeling from physical to digital, allow for more precise and manipulable representations.
The introduction of CAD software dramatically enhanced the accuracy and efficiency of architectural models. Today, digital modeling is indispensable in architecture, used from the earliest conceptual phases to the final stages of design.
The period of the late 1990s and early 2000s was marked by advances in digital and construction technology that enabled architects to express and realize forms that could only have been conceptualized previously.
The global 3D printing construction market size is expected to grow from $1.094 billion in 2021 to $585.84 billion by 2030
This evolution reflects broader trends in technology adoption across industries, demonstrating a continual push toward digital solutions that enhance productivity and creativity.

Traditional vs. Modern Techniques in Architectural Model Making
Statistics show that the use of 3D visualization in architecture has led to a 45% reduction in project turnaround times, due to faster decision-making and fewer revisions.
Traditional Handcrafted Models
Traditionally, architectural models were created by hand using a variety of materials like wood, cardboard, and plastic. This method required meticulous craftsmanship and could take weeks or even months to complete, depending on the project’s complexity.
While these models provided a tangible, three-dimensional representation of architectural ideas, their creation was labor-intensive and time-consuming. The precision of these models largely depended on the skill of the craftsman, leading to potential inaccuracies in scale and detail.
Modern 3D Architectural Modeling
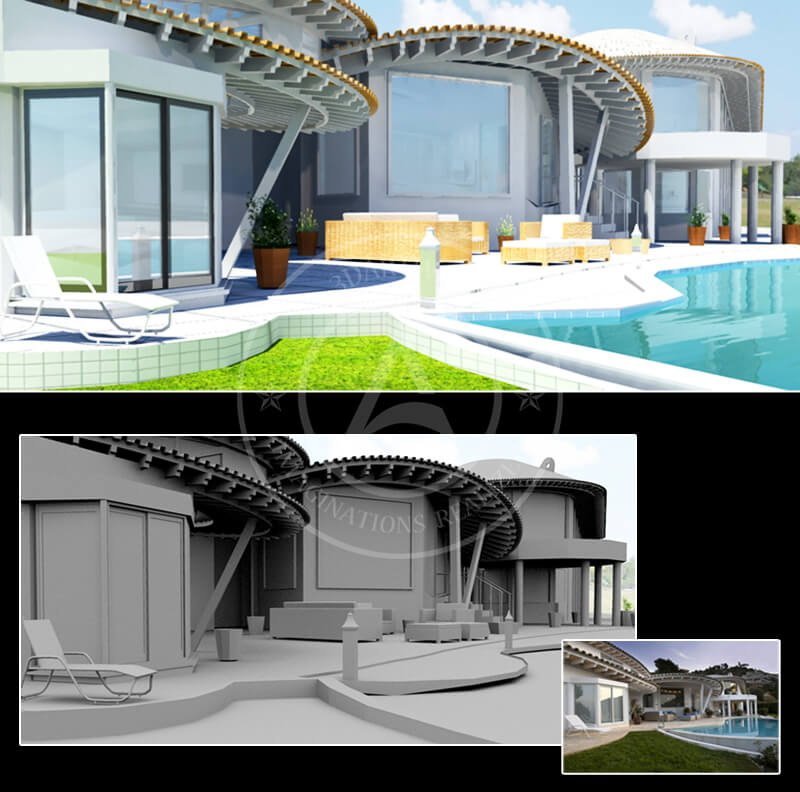
With the advent of 3D modeling technology, the field of architectural model making has witnessed a significant transformation. Modern 3D architectural modeling involves the use of computer software to create digital representations of buildings. These models are not only quicker to produce but also offer greater accuracy and flexibility. Changes to designs can be made in real-time, allowing architects and clients to experiment with different configurations more efficiently.

Advantages of Digital Techniques Over Conventional Methods
By enabling virtual walkthroughs and real-time modifications, 3D architectural design tools are setting new standards in efficiency and client satisfaction:
- Speed: Digital models can be developed much faster than traditional models. Changes and iterations that once took days can now be completed in hours.
- Accuracy: Digital tools offer precision that handcrafting can’t match, ensuring that the scale and dimensions are perfectly replicated.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in 3D modeling software can be significant, the ability to make quick modifications saves money in the long run by reducing the need for physical materials and labor.
- Visualization: 3D models provide immersive experiences through virtual reality or augmented reality, allowing for a better understanding of how a space works before it’s built.
- Integration: Digital models easily integrate with other digital tools and systems, facilitating better collaboration among construction teams and stakeholders.
The Future of 3D Printing and Architectural Model Making
The trajectory of 3D printing in architecture points toward even more innovative and transformative changes. Industry experts predict that within the next decade, the use of 3D printing will expand beyond small models to full-scale construction projects, with techniques capable of printing entire buildings or complex structural elements directly on site.
This advancement is expected to further reduce construction time and costs, while also increasing the potential for customization in architectural design.
97% of manufacturers expect their use of 3D printing to grow within the next five years, with most expecting it to at least double.
Potential for New Materials and Methods
The exploration of new materials is also at the forefront of future developments in 3D printing. Researchers are currently experimenting with eco-friendly materials like recycled plastics and composites that could offer enhanced sustainability without compromising structural integrity.
Moreover, the integration of smart materials, which can adapt to environmental changes, is set to redefine the functionalities of buildings, making them more energy-efficient and responsive to occupants’ needs.
Conclusion
The transformative potential of 3D printing and modeling in architecture is undeniable. These technologies offer architects unparalleled precision, efficiency, and flexibility, revolutionizing everything from initial design stages to final construction processes.
With the ability to reduce costs, enhance sustainability, and unlock new creative possibilities, 3D technologies are reshaping the architectural landscape. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing these advancements is crucial for any firm looking to lead in innovation and design excellence.
Interested in integrating 3D printing and modeling into your projects? Contact 3DArtway today to explore how we can elevate your architectural capabilities to new heights.